Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, is essential for fatty acid synthesis, amino acid metabolism, and glucose generation, while supplementation may reinforce hair health, promote nail strength, support healthy skin, and assist with blood sugar regulation.
Biotin is a coenzyme that is also known by other common names such as coenzyme R, vitamin B7 and vitamin H. It has eight specific forms, but only D-biotin is completely biologically active in humans. The general term “biotin” therefore refers specifically to D-biotin unless otherwise stated.
Biotin is an essential human nutrient that is required for various biochemical processes such as the synthesis of fatty acids, catabolism of amino acids and generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources. Biotin generally accomplishes these tasks by attaching to proteins at certain sites in a biochemical process known as biotinylation. This process is routinely used in the laboratory to study activities such as protein interactions, protein localization and DNA transcription.
Humans are not able directly biosynthesize biotin, although bacteria that normally reside in the intestines usually produce enough sufficient biotin to meet the body’s requirements. Biotin is also available from many dietary sources, especially leafy green vegetables such as kale, spinach and Swiss chard. Additional sources of biotin include peanuts, liver and raw egg yolks. A nutritional deficiency of biotin is very rare and normally occurs only in specific circumstances.
Biotin is also readily available as a dietary supplement. Moses Wolf Goldberg and Leo Sternbach developed a process for synthesizing biotin during the 1940s. The precursor in this process is fumaric acid, which is still used for the commercial production of biotin.
Biotin supplements are often used to strengthen nails and hair. Many health products also contain biotin, especially those used for hair and skin care. In addition, biotin can be found in many cosmetic products.
The most common uses of biotin in health supplements are for hair and skin health. It is also used to support nail growth and help support the body’s natural ability to manage and regulate blood sugar levels.
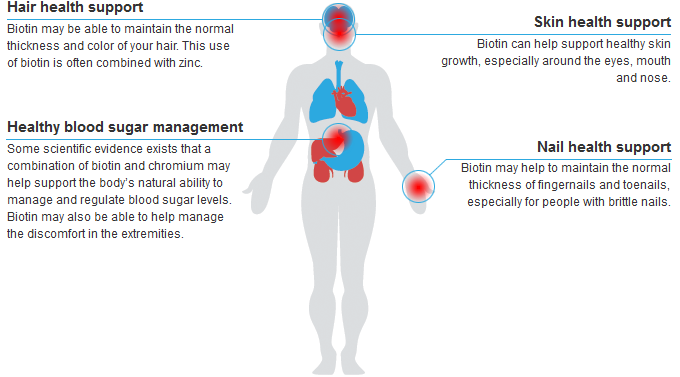
Biotin may be able to maintain the normal thickness and color of your hair. This use of biotin is often combined with zinc.
Some scientific evidence exists that combining biotin and chromium may help support the body’s natural ability to manage and regulate blood sugar levels. Biotin may also be able to help manage the discomfort in the extremities.
Biotin can help support healthy skin growth, especially around the eyes, mouth, and nose.
Biotin may help to maintain the normal thickness of fingernails and toenails,
especially for people with brittle nails.
A biotin deficiency is most likely to occur under conditions such as malnutrition, pregnancy, rapid weight loss and long-term tube feeding. This deficiency may also result from an imbalance of intestinal bacteria or various genetic defects. The most significant physical signs of a biotin deficiency primarily consist of hair loss and a red, scaly skin rash. Even a slight biotin deficiency may also cause psychological signs such as low moods and lethargy. Additional signs that you may need biotin supplements include tingling and numbness of the extremities.
D-biotin, coenzyme R, vitamin B7, vitamin H
Shipping calculated at checkout
